Prefixes – Explaination and Exampls
Understanding Prefixes:
A prefix is placed at the start of a word to modify its meaning. Prefixes often indicate negation, direction, time, location, or quantity. They can completely alter the meaning of the root word, making them powerful tools for expanding your vocabulary.
How Prefixes Work:
When a prefix is attached to the beginning of a word, it changes the word’s meaning. For example, the prefix “un” added to the word “happy” forms “unhappy,” which means not happy. Understanding common prefixes can help you interpret unfamiliar words and even create new ones.
50 Common Prefixes in English
Below is a list of 50 commonly used prefixes, along with their meanings and examples.
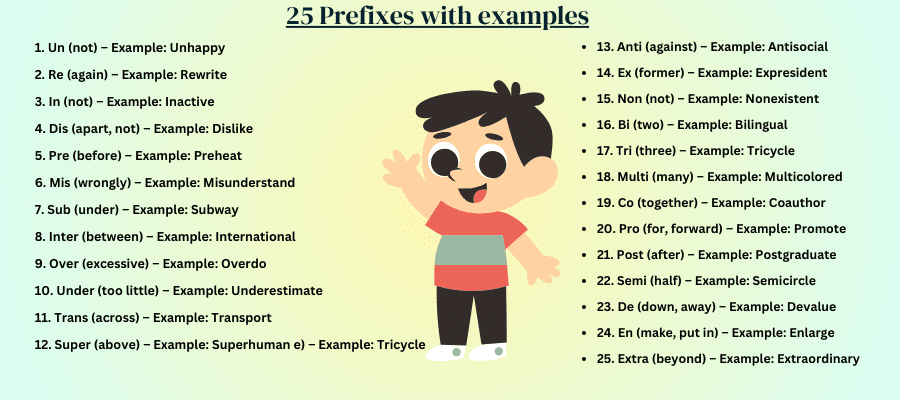
- Un (not) – Example: Unhappy
- Re (again) – Example: Rewrite
- In (not) – Example: Inactive
- Dis (apart, not) – Example: Dislike
- Pre (before) – Example: Preheat
- Mis (wrongly) – Example: Misunderstand
- Sub (under) – Example: Subway
- Inter (between) – Example: International
- Over (excessive) – Example: Overdo
- Under (too little) – Example: Underestimate
- Trans (across) – Example: Transport
- Super (above) – Example: Superhuman
- Anti (against) – Example: Antisocial
- Ex (former) – Example: Expresident
- Non (not) – Example: Nonexistent
- Bi (two) – Example: Bilingual
- Tri (three) – Example: Tricycle
- Multi (many) – Example: Multicolored
- Co (together) – Example: Coauthor
- Pro (for, forward) – Example: Promote
- Post (after) – Example: Postgraduate
- Semi (half) – Example: Semicircle
- De (down, away) – Example: Devalue
- En (make, put in) – Example: Enlarge
- Extra (beyond) – Example: Extraordinary
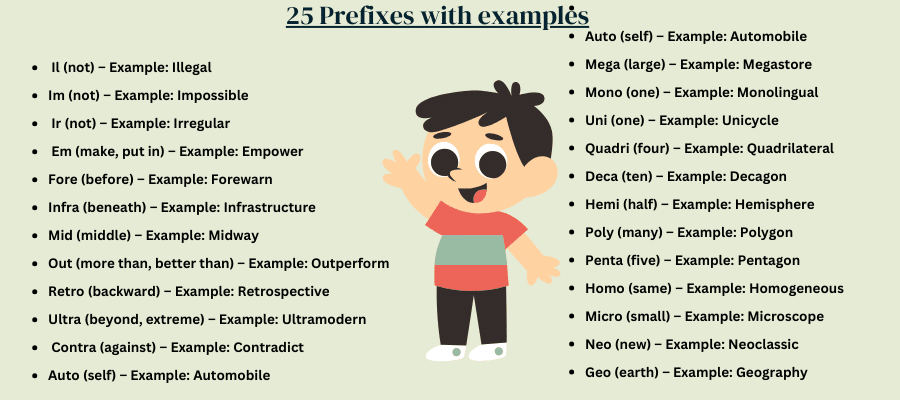
- Il (not) – Example: Illegal
- Im (not) – Example: Impossible
- Ir (not) – Example: Irregular
- Em (make, put in) – Example: Empower
- Fore (before) – Example: Forewarn
- Infra (beneath) – Example: Infrastructure
- Mid (middle) – Example: Midway
- Out (more than, better than) – Example: Outperform
- Retro (backward) – Example: Retrospective
- Ultra (beyond, extreme) – Example: Ultramodern
- Contra (against) – Example: Contradict
- Auto (self) – Example: Automobile
- Mega (large) – Example: Megastore
- Mono (one) – Example: Monolingual
- Uni (one) – Example: Unicycle
- Quadri (four) – Example: Quadrilateral
- Deca (ten) – Example: Decagon
- Hemi (half) – Example: Hemisphere
- Poly (many) – Example: Polygon
- Penta (five) – Example: Pentagon
- Homo (same) – Example: Homogeneous
- Micro (small) – Example: Microscope
- Neo (new) – Example: Neoclassic
- Geo (earth) – Example: Geography