Suffixes – All you need to know
Understanding Suffixes
A suffix is a letter or group of letters added at the end of a word to change its form or meaning. Suffixes often help to create different parts of speech, such as turning a noun into an adjective, verb, or adverb. They can also indicate tense, plurality, or possession.
How Suffixes Work:
Suffixes are used to modify the meaning or grammatical function of a root word. For example, adding the suffix “ful” to the word “joy” forms “joyful,” which means full of joy. Understanding suffixes helps in both building vocabulary and improving grammar.
50 Common Suffixes in English
Below is a list of 50 commonly used suffixes, along with their meanings and examples.
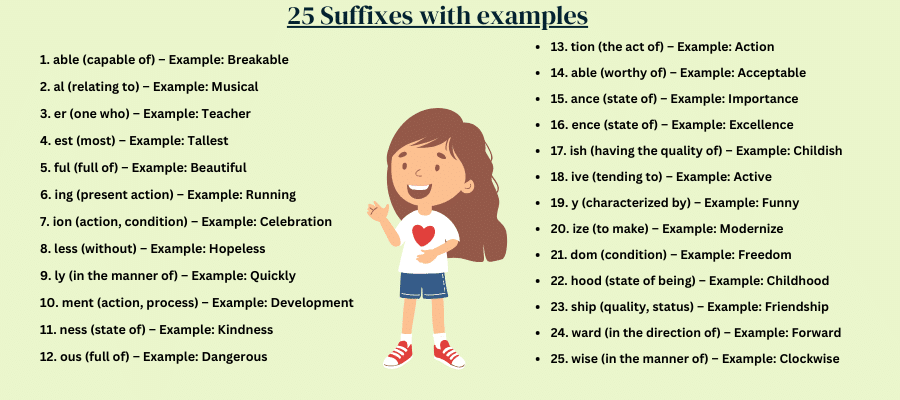
- able (capable of) – Example: Breakable
- al (relating to) – Example: Musical
- er (one who) – Example: Teacher
- est (most) – Example: Tallest
- ful (full of) – Example: Beautiful
- ing (present action) – Example: Running
- ion (action, condition) – Example: Celebration
- less (without) – Example: Hopeless
- ly (in the manner of) – Example: Quickly
- ment (action, process) – Example: Development
- ness (state of) – Example: Kindness
- ous (full of) – Example: Dangerous
- tion (the act of) – Example: Action
- able (worthy of) – Example: Acceptable
- ance (state of) – Example: Importance
- ence (state of) – Example: Excellence
- ish (having the quality of) – Example: Childish
- ive (tending to) – Example: Active
- y (characterized by) – Example: Funny
- ize (to make) – Example: Modernize
- dom (condition) – Example: Freedom
- hood (state of being) – Example: Childhood
- ship (quality, status) – Example: Friendship
- ward (in the direction of) – Example: Forward
- wise (in the manner of) – Example: Clockwise
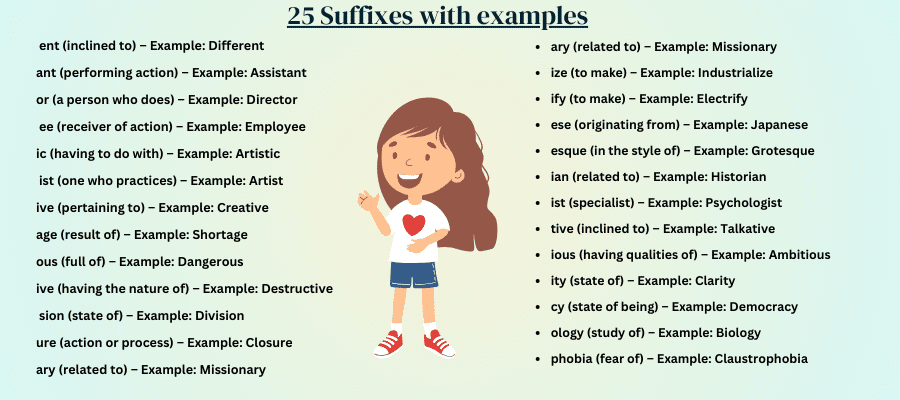
- ent (inclined to) – Example: Different
- ant (performing action) – Example: Assistant
- or (a person who does) – Example: Director
- ee (receiver of action) – Example: Employee
- ic (having to do with) – Example: Artistic
- ist (one who practices) – Example: Artist
- ive (pertaining to) – Example: Creative
- age (result of) – Example: Shortage
- ous (full of) – Example: Dangerous
- ive (having the nature of) – Example: Destructive
- sion (state of) – Example: Division
- ure (action or process) – Example: Closure
- ary (related to) – Example: Missionary
- ize (to make) – Example: Industrialize
- ify (to make) – Example: Electrify
- ese (originating from) – Example: Japanese
- esque (in the style of) – Example: Grotesque
- ian (related to) – Example: Historian
- ist (specialist) – Example: Psychologist
- tive (inclined to) – Example: Talkative
- ious (having qualities of) – Example: Ambitious
- ity (state of) – Example: Clarity
- cy (state of being) – Example: Democracy
- ology (study of) – Example: Biology
- phobia (fear of) – Example: Claustrophobia
Conclusion
Learning prefixes and suffixes can greatly enhance your understanding of the English language. By knowing how to break down complex words into their root forms, prefixes, and suffixes, you will be better equipped to expand your vocabulary and improve your communication skills. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or just someone looking to improve your English, these word parts will help you decipher new words and create more precise language in both writing and speech.